ICT
ICT
Vision
Every staff and student are competent in the use of ICT to carry out self-directed and collaborative learning in a safe and responsible manner.
Mission
Enhance the ICT environment that supports and guides all staff and students to be engaged in teaching and learning.
ICT Department Programmes
A comprehensive ICT Baseline Skills programme has been implemented to equip students with essential digital competencies. This initiative encompasses fundamental login procedures and navigation of the Student Learning Space (SLS) interface, as well as familiarisation with the Zoom platform, enabling students to participate independently in Home-Based Learning (HBL) sessions.
As students’ progress, they develop touch typing proficiency and are introduced to basic video editing techniques. These skills are designed to prepare our learners for the increasingly technology-driven society that they will encounter, positioning them well to adapt to and thrive in future academic and professional environments.
Furthermore, coding has been incorporated into our STEM curriculum. This aspect of the programme emphasises practical application, demonstrating real-world relevance while maintaining an engaging and enjoyable learning experience. By mastering these digital tools, our students will be well-prepared to apply their skills in various contexts as they navigate our technology-driven society in the near future.

During our students’ schooling years with us, we will complement our ICT lessons with the National Literacy Programme which covers digital literacy, digital competencies and the technological skills. This is to ensure that students are well-equipped with the digital competencies to thrive in an increasingly technology-saturated future.
Digital literacy
Digital literacy is defined as a set of knowledge, skills and dispositions that would help our learners to be confident, critical and responsible users of digital technologies. MOE’s National Digital Literacy Programme was launched in March 2020 for our schools and Institutes of Higher Learning. Under the programme, students will acquire digital skills across four components in the “Find, Think, Apply, Create” framework.
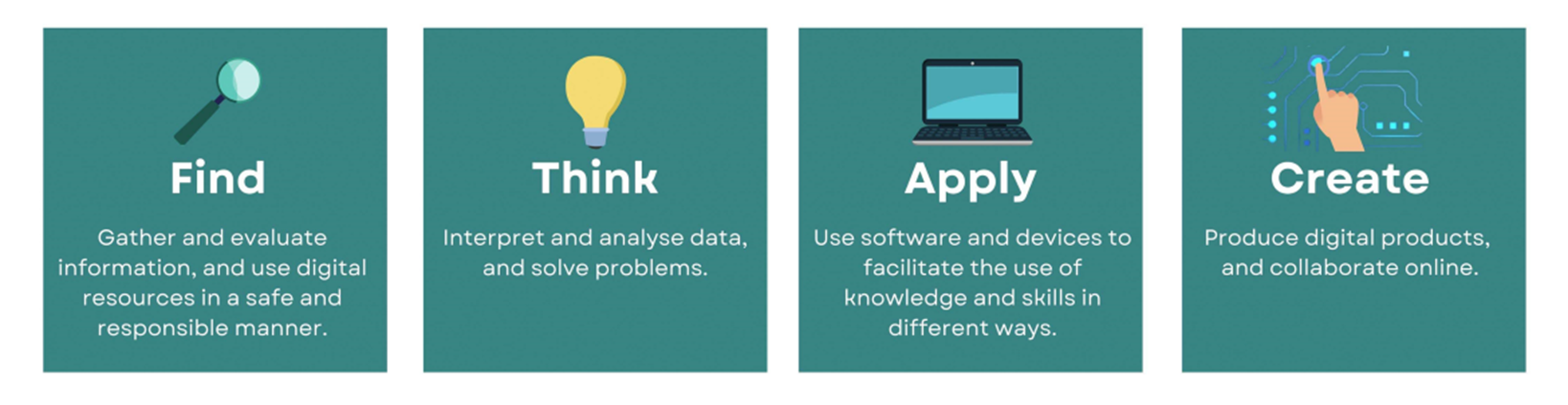
Digital competencies
Under the EdTech Masterplan 2030, the “Find, Think, Apply, Create” framework is further unpacked into 9 digital competencies to support deepening of digital literacy in schools.
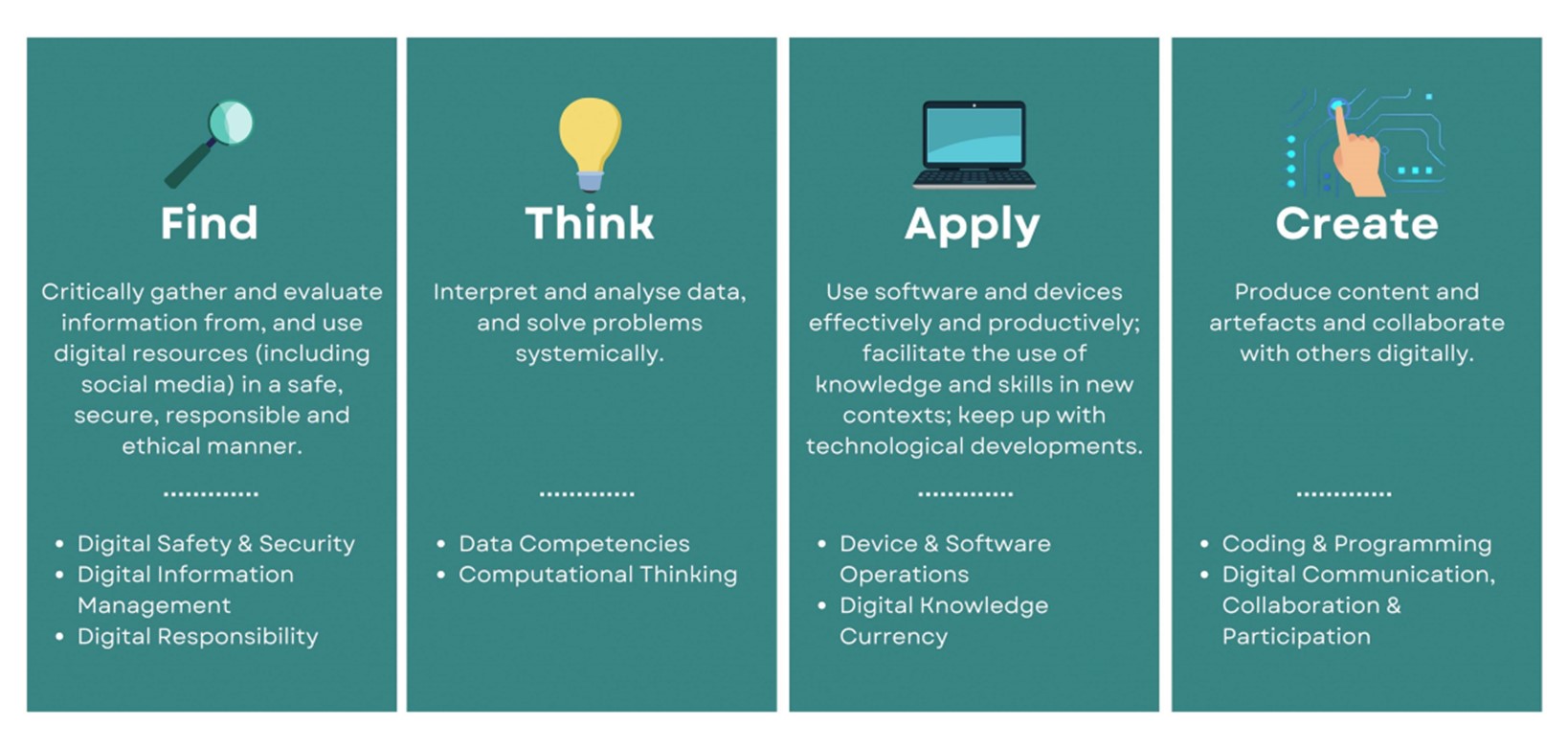
9 Digital Competencies covers:
1.Digital Safety & Security
Understanding of online behaviour and awareness of how to protect oneself in the online space.
2.Digital Responsibility
When navigating the online space, demonstrate respect for oneself and others, and practise safe, responsible and ethical use.
3.Digital Knowledge Currency
Keep oneself up-to-date with technological developments and the use of digital resources as part of learning for life.
4.Computational Thinking
Employ computational thinking together with technological tools to solve problems e.g. when developing and testing solutions.
5.Digital Information Management
Employ effective strategies to locate information and resources, and exercise discernment by evaluating the accuracy, credibility, and relevance of information. Distil and synthesise essential content from the often large amount of information available online.
6.Digital Communication, Collaboration & Participation
Leverage digital platforms and tools to communicate ideas, connect with others and contribute constructively to a common goal.
7.Data Competencies
Read, understand, interpret, manipulate, analyse and present data in meaningful ways.
8.Device & Software Operations
Understand how devices and software work in order to use them effectively and productively.
9.Coding & Programming
Utilise a variety of digital methods such as block-based programming, text-based programming, prompt engineering to create digital artefacts or to develop, test and debug solutions.
Technological skills
Technological skills refer to the ability to understand and use specific technologies to solve problems and achieve practical goals.
Acceptable Use Policy
Purpose of the Acceptable Use Policy (AUP)
Technology is an essential part of learning in today’s world.
This Acceptable Use Policy (AUP) establishes guidelines on the appropriate use of EdTech resources to help you understand how to use these resources safely and responsibly, in line with efforts to develop your digital literacies and growth as digitally responsible citizens.
EdTech resources include the following, but are not limited to:
- Learning devices (e.g. Personal Learning Devices (PLDs), school devices)
- ICT system accounts (e.g. Singapore Student Learning Space (SLS), iCON); and
school internet networks.
For more information, please refer to: Student Kit on Cyber Wellness and Learning with a Learning Device (Primary) – https://go.gov.sg/cw-studentkitpri
General
- You should not attempt to access data, system and information that you are not authorised to.
- You are reminded that the use of learning devices and school’s EdTech resources should solely be for the purpose of learning.
Being a Responsible Digital Citizen
- You should interact with others in a respectful and responsible way. You should not post online remarks that are
• racially and/or religiously insensitive,
• vulgar and/or offensive, or
• hurtful to others. - You should not use any devices to
• store, modify, create or share content (e.g. documents, presentations, pictures and videos) that is inappropriate (e.g. indecent, pornographic, defamatory, hurtful to self or others).
• make threats, cause harassment or embarrassment, impersonate or intimidate others. - You should not use MOE/school-deployed ICT system accounts for any commercial activities (e.g. buying and selling of goods and services).
Non-compliance with the above will lead to disciplinary action in accordance with the school’s discipline policy.
Respecting Copyright
- You are reminded to obtain explicit permission from the content owner(s) before downloading, copying or sharing any copyrighted materials (e.g. pictures, videos, music).
- You should not use, copy, edit or share digital files in an unauthorised or illegal manner.
Using Artificial Intelligence (AI)
- You must ensure that you meet the minimum age requirement specified in each AI tool’s age restrictions before using it.
- If the use of AI is permitted, you should acknowledge the use of AI in weighted assessments and homework as required.
- You are to practice academic integrity and be responsible for your own learning when using AI. Understand that you are ultimately short-changing yourself if you pass off other’s work as your own.
Staying Safe and Secure Online
- You should report any incidents (e.g. unusual device behaviour or inappropriate use of devices), to the school.
- You are reminded to develop online safety habits. This includes not disclosing personal access credentials (e.g. MIMS password, SLS password, etc.), sensitive personal data (e.g. home address, passwords) online or on AI platforms, verifying credibility of online content before sharing, avoiding clicking on suspicious links or downloading unknown files, and being cautious when interacting with others online (e.g. on social media) by not engaging with strangers.
- You should exercise caution regarding the limitations of AI tools, including potential inaccuracies / fabricated responses, inherent biases and outdated information.
Digital Wellbeing and Balance
- You are reminded to balance screentime with other activities including physical exercise and face-to-face social interactions.
- You should avoid excessive use of your devices outside learning hours.
- You should take regular breaks to rest your eyes and mind.
- You are reminded to practice good sleep hygiene by not using your devices one hour before bedtime.

